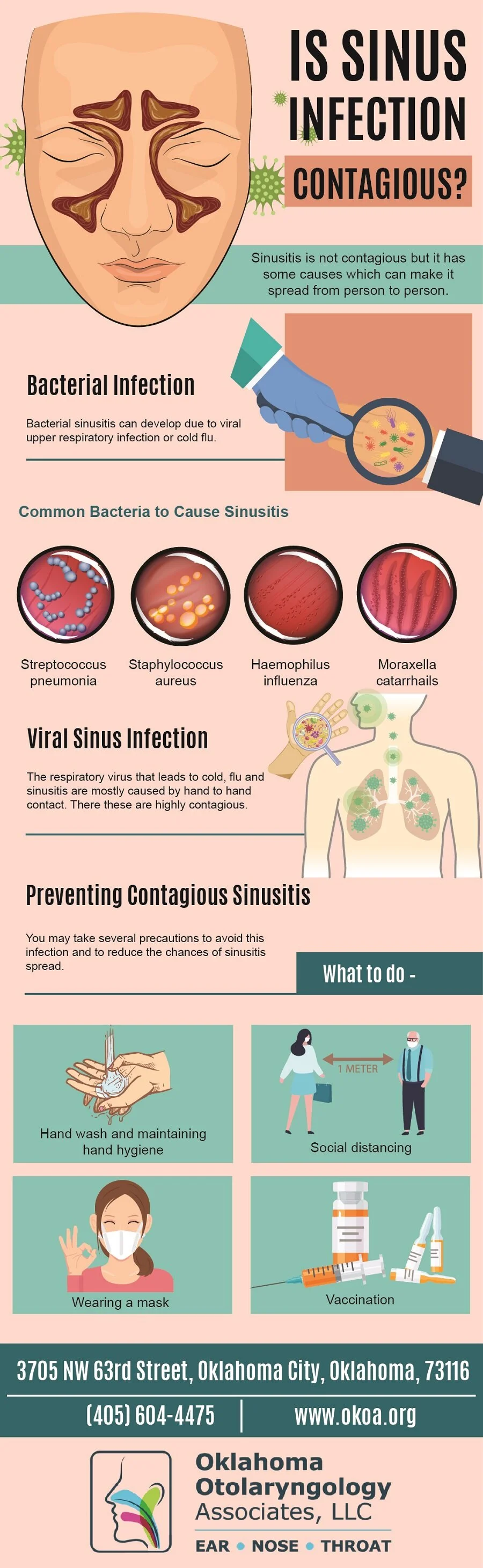
Sinus infections, a common medical condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, have long plagued both patients and healthcare professionals alike. As a prominent health site dedicated to delivering valuable information on phlebotomy and healthcare, we aim to shed light on the pressing question that often leaves individuals puzzled and concerned: are sinus infections contagious? In this article, we will provide a comprehensive analysis of this question, exploring various aspects of sinus infections, their transmission, and practical tips on prevention. By equipping readers with an in-depth understanding of this topic, we strive to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and wellbeing.
This image is property of images.squarespace-cdn.com.
What are sinus infections?
Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, are inflammation or infection of the sinuses – the air-filled cavities in the bones around the nose and eyes. This condition can cause a range of symptoms, including nasal congestion, facial pain or pressure, headache, cough, and post-nasal drip. Sinus infections can be acute, lasting for a few weeks, or chronic, lasting for more than twelve weeks.
Causes of sinus infections
Sinus infections can be caused by various factors. The most common cause is a viral infection, usually occurring after a person has a cold or flu. Other causes include bacterial infections, fungal infections, allergies, and structural issues such as nasal polyps or a deviated septum. It is important to identify the underlying cause to determine the most effective treatment approach.

This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
Contagiousness of sinus infections
Understanding contagion
Many people wonder if sinus infections are contagious. The contagiousness of sinus infections depends on the underlying cause. Viral sinus infections, which are the most common, are contagious and can be spread from person to person through respiratory droplets. Bacterial and fungal sinus infections are generally not contagious, as they are caused by an overgrowth of bacteria or fungi that are already present in the sinuses.
Mode of transmission
Viral sinus infections are primarily transmitted through close contact with an infected person. When an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or talks, respiratory droplets containing the virus can be inhaled by others. These droplets can also contaminate surfaces, and if touched, can lead to infection if the person then touches their nose or mouth.
Common misconceptions
Confusion with common cold
There is often confusion between sinus infections and the common cold, as they share similar symptoms. However, it is important to note that a sinus infection can develop as a complication of a cold. While a cold is usually caused by a viral infection that affects the entire respiratory system, sinus infections specifically target the sinuses.
Bacterial vs. viral sinus infections
Another common misconception is that all sinus infections are caused by bacteria. In reality, the majority of sinus infections are caused by viruses, particularly after a cold. Bacterial sinus infections, although less common, occur when bacteria invade the sinuses, often due to a weakened immune system or an obstruction in the sinuses.

This image is property of d2zbzumnfle0rf.cloudfront.net.
Bacterial sinus infections
Overview of bacterial sinus infections
Bacterial sinus infections occur when bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae, invade the sinuses. These infections are less common than viral sinus infections but are typically more severe and may require medical intervention. Symptoms of bacterial sinus infections may include facial swelling, thick yellow or green nasal discharge, persistent pain or pressure, and fever.
Contagiousness of bacterial sinus infections
Bacterial sinus infections themselves are not contagious. However, the bacteria causing the infection can be transmitted through close contact with an infected individual. Therefore, it is crucial to practice good hygiene and avoid sharing personal items, such as towels or eating utensils, to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Prevention and treatment
Preventing bacterial sinus infections involves maintaining good hygiene, such as regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections. Treatment for bacterial sinus infections may involve the use of antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
Viral sinus infections
Overview of viral sinus infections
Viral sinus infections are the most common type of sinus infection and are typically caused by viruses, such as rhinovirus or influenza virus. These infections often develop as a complication of the common cold or flu. Symptoms of viral sinus infections are similar to those of bacterial sinus infections and may include nasal congestion, facial pain, headaches, and fatigue.
Contagiousness of viral sinus infections
Viral sinus infections are contagious and can be easily transmitted from person to person. The viruses responsible for causing the infection can spread through respiratory droplets when an infected individual coughs or sneezes. Avoiding close contact with infected individuals, practicing good respiratory hygiene, and frequently washing hands can help reduce the risk of viral sinus infections.
Prevention and treatment
Prevention of viral sinus infections involves similar measures as preventing the common cold or flu. These include practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and getting vaccinated against the flu. Treatment for viral sinus infections focuses on symptom management and may include over-the-counter pain relievers, decongestants, saline nasal sprays, and rest.

This image is property of www.nasoneb.com.
Fungal sinus infections
Overview of fungal sinus infections
Fungal sinus infections are rare and typically occur in individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS. They can also develop in individuals who are exposed to environmental fungi, such as Aspergillus or Mucor. Symptoms of fungal sinus infections can include facial pain, nasal congestion, and persistent headache.
Contagiousness of fungal sinus infections
Unlike viral and bacterial sinus infections, fungal sinus infections are not contagious and cannot spread from person to person. Fungi that cause these infections are commonly found in the environment and do not rely on human transmission. However, individuals with weakened immune systems should take precautions to minimize exposure to fungal spores.
Prevention and treatment
Preventing fungal sinus infections involves minimizing exposure to environmental fungi, especially for individuals with compromised immune systems. This can be achieved by keeping indoor environments clean and well-ventilated, avoiding areas with mold or dampness, and using air purifiers if necessary. Treatment for fungal sinus infections often requires antifungal medications, which may be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Duration of contagiousness
Length of contagious period
The contagious period of sinus infections varies depending on the underlying cause. Viral sinus infections are typically contagious for as long as the individual is experiencing symptoms, which can last for about a week or two. Bacterial sinus infections, once antibiotic treatment has been initiated, are generally no longer contagious after 24 to 48 hours. Fungal sinus infections are not contagious at any stage.
Factors affecting contagiousness
Several factors can influence the contagiousness of sinus infections. These include the individual’s immune system response, the type of infection, and the effectiveness of preventive measures taken. Proper hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals can significantly reduce the risk of transmitting or acquiring sinus infections.

This image is property of www.drneetumodgil.com.
Preventing sinus infections
Maintaining good hygiene
Practicing good hygiene is essential in preventing sinus infections. This includes regular handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching surfaces that may be contaminated. Using hand sanitizers containing at least 60% alcohol when soap and water are not available can also help reduce the spread of infections.
Boosting immune system
Maintaining a healthy immune system can help prevent sinus infections. This can be achieved through a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and managing stress levels. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also important for a strong immune system.
Avoiding exposure to allergens
Allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, can trigger sinusitis in individuals with allergies. Taking measures to reduce exposure to these allergens, such as using air purifiers, keeping indoor environments clean, and avoiding known triggers, can help prevent sinus infections associated with allergies.
Managing and treating sinus infections
Seeking medical advice
If symptoms of a sinus infection persist for an extended period or worsen despite self-care measures, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can assess the severity of the infection, identify the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatment options. They may also perform imaging tests or collect samples for further analysis if necessary.
Medications for sinus infections
The treatment approach for sinus infections depends on the underlying cause. In the case of bacterial sinus infections, antibiotics are commonly prescribed to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Viral sinus infections do not respond to antibiotics, and treatment usually focuses on symptom management with over-the-counter pain relievers, decongestants, and nasal sprays. Fungal sinus infections often require antifungal medications.
Home remedies and self-care
In addition to medical treatment, various home remedies and self-care measures can help manage the symptoms of sinus infections. Nasal irrigation with saline solutions, using warm compresses on the face, staying hydrated, inhaling steam, and getting sufficient rest can provide relief and promote healing. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any home remedies, especially in severe or persistent cases.
When to seek medical help
Persistent or severe symptoms
While most sinus infections resolve on their own or with appropriate treatment, there are instances where medical attention is necessary. If symptoms persist for more than a week or worsen despite self-care measures, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, severe symptoms such as high fever, severe facial pain, swelling, or changes in vision should prompt immediate medical attention.
Complications of untreated sinus infections
Untreated or inadequately treated sinus infections can lead to complications. These complications can include the spread of infection to nearby structures, such as the eyes or brain, development of chronic sinusitis, the formation of abscesses, and the worsening of underlying conditions, such as asthma or allergies. Seeking timely medical help and following the recommended treatment can help prevent the occurrence of these complications.
In conclusion, sinus infections can be caused by various factors including viruses, bacteria, and fungi. While viral sinus infections are contagious and can be spread through respiratory droplets, bacterial and fungal sinus infections are typically not contagious. Preventive measures such as maintaining good hygiene, boosting the immune system, and avoiding exposure to allergens can help reduce the risk of sinus infections. Managing and treating sinus infections involve seeking medical advice, taking appropriate medications, and utilizing home remedies for symptom relief. It is important to seek medical help if symptoms persist or worsen, as untreated sinus infections can lead to complications.